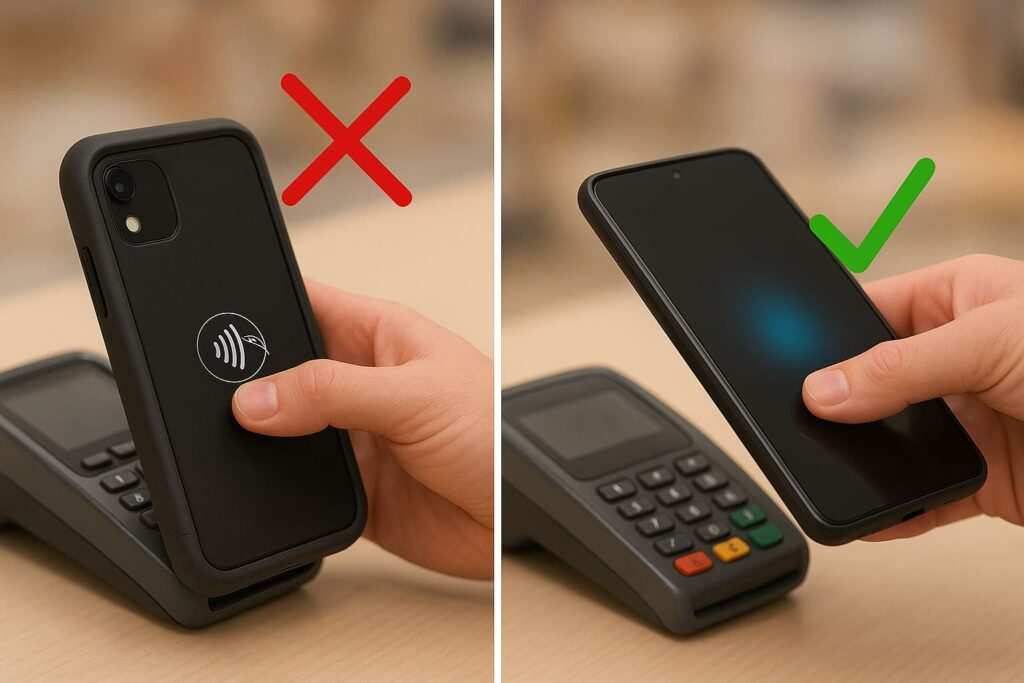
It’s a frustrating moment: you tap your phone to pay for coffee or scan an NFC tag, and… nothing happens. You pop off the case, try again, and it works perfectly. Why does your card or tag only work without a case?
The problem is usually caused by your case being too thick, containing metal, or having magnets that interfere with your phone’s contactless technology. This guide will explain the science behind the failure and give you simple, step-by-step fixes for Apple Pay, Google Wallet, and NFC tags.
Quick Test: Is Your Case the Problem?
Not sure if your case is the culprit? Follow these three simple steps to diagnose the issue in 60 seconds.
- Enable Contactless: On Android, swipe down and ensure the NFC icon is turned on in your quick settings. On iPhone, wake the screen and double-click the side button to arm Apple Pay (or just bring the top of iPhone to the reader when prompted).
- Test Without the Case: Remove your phone case completely and try tapping to pay or scanning an NFC tag. If it works instantly, the case is the problem.
- Test With the Case: Put the case back on. Try tapping again, making sure to align the correct part of your phone with the reader. If it fails again, you’ve confirmed the case is blocking the signal.
Why Your Card Only Works Without a Case (Metal Case NFC and Thick Case NFC)
Your phone uses Near Field Communication (NFC) to talk to payment terminals and tags. This technology relies on a delicate, low-power magnetic field. When something disrupts that field, the connection fails.
The Physics of NFC Failure: A Quick Primer
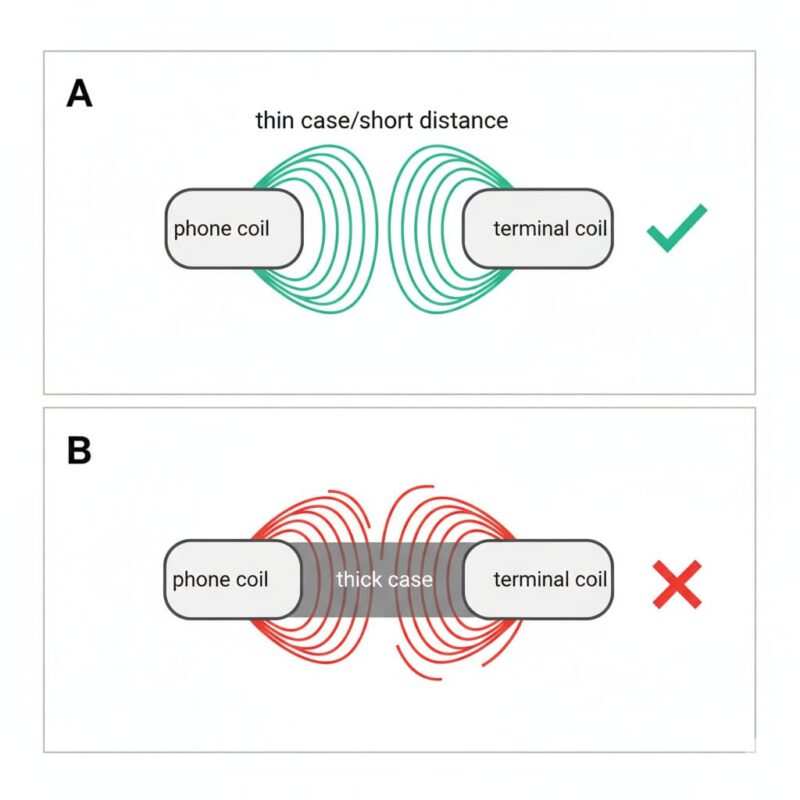
NFC works through a process called magnetic coupling. Your phone’s internal NFC antenna creates a small magnetic field, and when it gets close to a terminal or tag, it induces an electrical current in the tag’s antenna, allowing them to exchange data at 13.56 MHz. This happens over a very short distance—typically within about 4 cm (≈1.6 in), though the exact NFC reading distance can vary. Two things commonly break this connection:
- Excessive Distance (Thick Cases): A thick phone case physically increases the distance between your phone’s NFC antenna and the reader. The magnetic field’s strength drops off very quickly with distance. Even a few extra millimeters from a rugged case can be enough to weaken the field so much that the connection fails.
- Signal Interference (Metal & Magnets): Metal is the biggest enemy of NFC. A metal plate or kickstand in your case creates disruptive electrical whirlpools called eddy currents when exposed to the NFC field. These currents generate their own magnetic fields that cancel out or scramble your phone’s signal. This is called detuning, and it effectively makes your phone’s antenna “deaf” to the terminal. MagSafe‑style magnets aren’t the main issue—the nearby metal ring/plate and extra stack height reduce coupling and detune the antenna.
Common Case Materials That Cause Problems
- Metal Plates: Often embedded for magnetic car mounts.
- Thick, Multi-Layered “Tough” Cases: The combined thickness of plastic, rubber, and air gaps can be too much.
- Battery Cases: The internal electronics and the battery itself can interfere with the NFC antenna.
- Cases with Metallic Paint or Liquid Glitter: Dense metallic particles can be enough to disrupt the signal.
Could It Be Something Else?
While the case is the culprit 99% of the time, very rarely the issue could be a software bug or a damaged NFC antenna in your phone. If NFC fails to work even with the case off, you may be facing a different issue. For device-specific troubleshooting, see our guides on how to fix an iPhone not reading NFC or what to do when Android says it couldn’t read a tag.
Quick Fixes When NFC Is Not Working With a Case
Here are the best ways to solve the problem, starting with the easiest and most effective fixes.
Restart Your Phone (The Simplest Fix)
Before trying anything else, perform a simple restart. Sometimes, the NFC service on your phone can get stuck, and a quick reboot is all it takes to get it working again.
- Why this works: Restarting clears temporary memory and resets all of your phone’s software components, including the NFC controller.
Reposition for the NFC Antenna Location (iPhone/Android)
You have to hit the “sweet spot.” The NFC antenna isn’t in the center of your phone. If you don’t align it correctly, the tap can fail even without a case.
- iPhone: The antenna is at the top edge of the phone’s back. Hold the top of your iPhone flat against the middle of the reader.
- Android (Google Pixel/Samsung Galaxy): The antenna is usually on the upper-back of the device. Move your phone slowly over the reader until you feel a vibration or see a checkmark on the screen.
- Why this works: The NFC field is strongest right at the antenna’s location. Aligning it perfectly ensures the maximum signal strength reaches the reader.
Remove Thick or Magnetic Cases and Retest
This is the simplest diagnostic test and often the most permanent solution. If NFC works perfectly without the case, you may need a slimmer, non-metallic case for reliable everyday use.
- Why this works: This removes the two biggest causes of failure: physical distance and metallic interference.
Apple Pay Not Working With a Case? Try the Top-of-iPhone Placement
For Apple Pay, the most common mistake is tapping the middle of the phone to the reader. You don’t need to fully unlock or open Wallet first. Double‑click the side button to arm Apple Pay (Face ID/Touch ID will authenticate), then hold the top of iPhone to the reader. If you’re still having trouble after correcting your placement, there might be other software or hardware issues at play. For a deeper dive, check out our complete guide on how to fix an iPhone not reading NFC.
- Why this works: This is simply a matter of correct positioning to align with the hardware’s location.
Google Wallet Not Working With a Case? Unlock and Check Settings
For Google Wallet on a Pixel or Samsung device, check three critical settings:
- NFC is On: Go to
Settings > Connected Devices > Connection preferences > NFC(on Pixel) orSettings > Connections > NFC and contactless payments(on Samsung) and make sure it’s toggled on. On Samsung, also set a default underNFC and contactless payments > Contactless payments. On other Android phones, checkSettings > Apps > Default apps > Tap & pay(name/path can vary). - Unlock Your Phone for Payments: Many Android devices have a security feature called Secure NFC (or “Require device unlock for NFC”). If this is enabled, you must unlock your phone just before you tap to pay or read an NFC tag. Leaving this feature on improves security by preventing unauthorized scans, but it does add an extra step to the process.
If your settings are correct but the problem persists, you might see an error like “couldn’t read tag.” Our guide on fixing Android tag reading errors can provide more advanced solutions.
- Why this works: Android gives users more control, but these settings must be enabled for payments to function. The “Secure NFC” feature is a trade-off: it adds security but requires an extra step.
Add a Ferrite Shim Between the Tag and Your Case
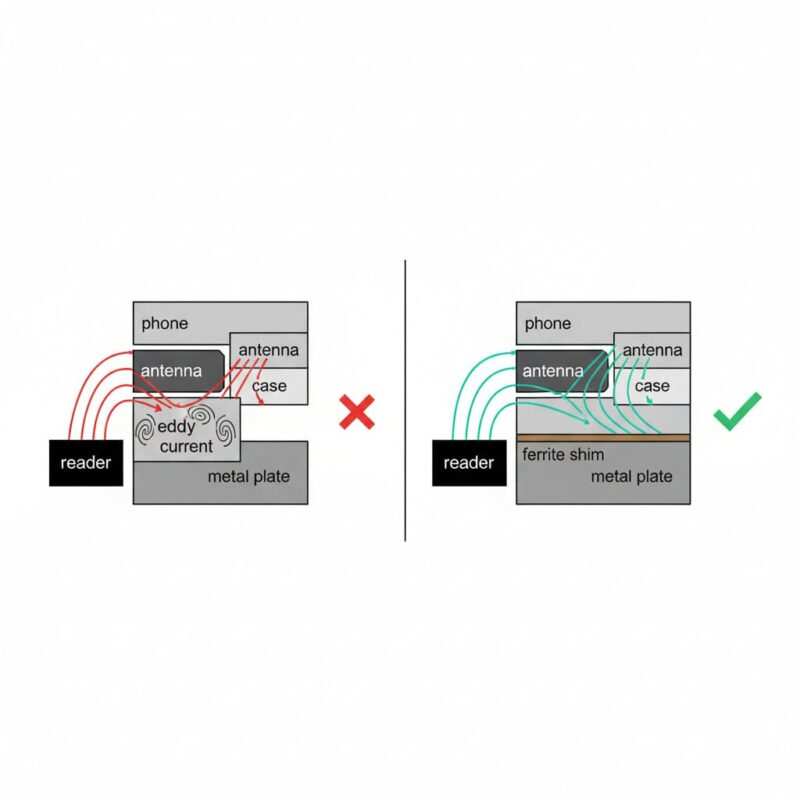
If your case has a metal plate you can’t part with, a ferrite shim can be a great fix. This is a thin, flexible sticker made of ferrite material that absorbs magnetic interference. Place it inside your case, directly between the metal plate and where your phone’s NFC antenna sits.
- Why this works: The ferrite material is specifically designed to absorb and redirect the disruptive eddy currents created by metal, effectively shielding your phone’s NFC antenna.
Avoid Stacked Cards Inside a Wallet Case
A wallet case with multiple cards is a double-whammy for NFC. The cards add physical thickness, and their own metallic chips and antennas create a messy field of signal interference. Stacked cards can also ‘present’ to the terminal and confuse selection—remove extras before tapping. Before you tap to pay with your phone, remove any extra contactless cards from the case.
- Why this works: Multiple NFC chips held close together can interfere with each other, confusing the payment terminal which doesn’t know which card to read.
Check for Software Updates
Sometimes, an NFC issue can be caused by a bug in your phone’s operating system (iOS or Android). Check for and install any available software updates, as they often contain bug fixes and performance improvements for core hardware functions like NFC.
- Why this works: Manufacturers often release patches that improve the performance and reliability of hardware components, including the NFC chip.
MagSafe Wallet NFC Interference Explained
A MagSafe wallet can cause NFC interference because the magnets in the wallet’s alignment ring are located very close to the iPhone’s NFC antenna. This, combined with the extra thickness from the wallet and the cards inside it, is often enough to cause a payment to fail. While MagSafe itself doesn’t use NFC, its magnetic design can unfortunately disrupt it.
Solutions for MagSafe Users:
- Remove the wallet before tapping: This is Apple’s official recommendation and the most foolproof method. It completely eliminates both the magnetic and distance issues.
- Minimize card count: The fewer cards in your MagSafe wallet, the less thickness and interference you’ll have. A single card is much less likely to cause an issue than three.
- Choose a slim MagSafe case: A thinner case reduces the total distance between the phone’s antenna and the reader, which can sometimes be enough to establish a connection even with the wallet attached.
NFC Tag Not Working on Metal? Use an On-Metal NFC Tag
How Standard Tags Fail on Metal
When you place a standard NFC tag on a metal surface, the metal essentially absorbs and scrambles the tag’s signal. The eddy currents created in the metal surface prevent the tag from powering on and communicating, making it invisible to your phone.
How On-Metal Tags Solve the Problem
An on-metal NFC tag has a built-in layer of ferrite material that acts as a shield. This shield isolates the tag’s antenna from the metal surface, preventing interference and allowing the tag to communicate with a phone properly. Think of it as a soundproof booth that blocks out the “noise” from the metal. The type of tag chip, such as an NTAG213 vs. an NTAG216, also affects performance, but metal is a separate, more powerful blocker.
DIY Alternative: Create Spacing
If you don’t have an on-metal tag, you can sometimes make a standard tag work by creating a physical gap between it and the metal surface. Sticking the tag to a thick piece of plastic or a stack of foam mounting squares (at least 1/4 inch or 5-6mm thick) can provide enough separation to prevent interference.
Device Tips: iPhone NFC Not Working With Case vs. Pixel/Samsung
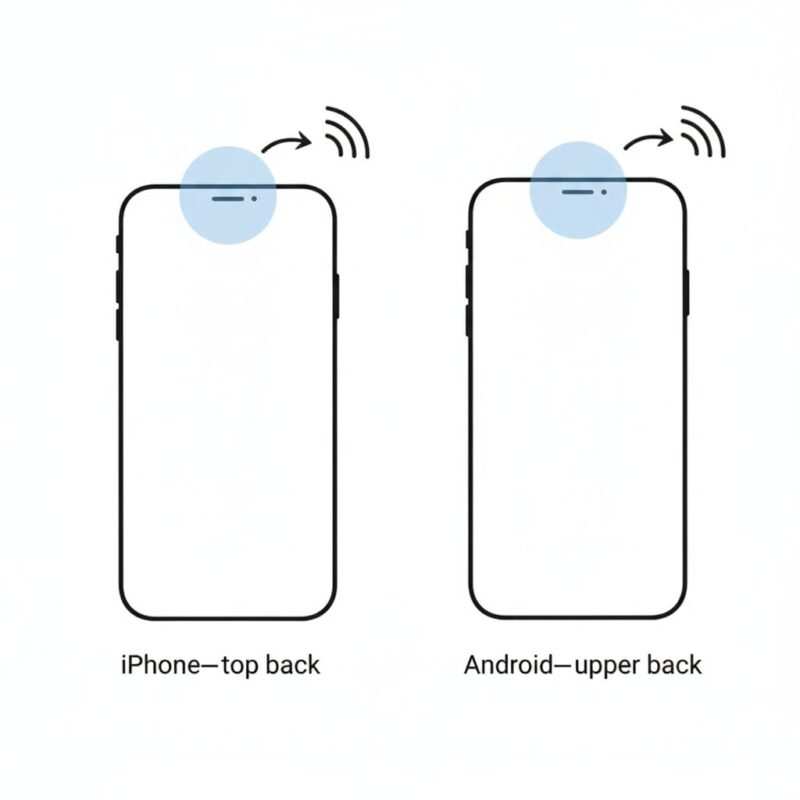
iPhone Tips (iPhone 12-16)
- Antenna Location: Near the top-back camera area.
- How to Use: Use the top-back edge. Double-click the side button to arm Apple Pay (Face ID/Touch ID prompts), then hold the top of your iPhone to the reader—no need to open Wallet first.
- Settings: There is no on/off toggle for NFC. It’s always on. iPhones XS and newer can read NFC tags in the background without needing an app open, making them great for NFC business cards.
Google Pixel & Samsung Galaxy Tips
- Antenna Location: Usually in the upper-back area. Some Android models show antenna placement hints in NFC settings—use them if available.
- How to Use: Enable NFC in settings, unlock your phone, and hold the back against the reader.
- Settings: You must turn on NFC manually in
Settings > Connections. With Secure NFC (or “Require device unlock for NFC”) enabled, you must unlock your phone for both tag reading and payments (card emulation). This prevents unauthorized scans when your phone is locked, improving security at the cost of an extra step. Android uses a system called Host Card Emulation (HCE), which allows apps like Google Wallet to securely mimic a physical card.
For a full breakdown of what works on each platform, see our complete compatibility guide for iPhone and Android.
How to Handle Thick and Metal Cases (Buyer’s Guide)
When shopping for a new case, use this checklist to ensure it will work with contactless payments.
What to Look For in an NFC-Friendly Case
- NFC-Compatible Label: Look for cases marketed as “NFC compatible,” “works with contactless payments,” or “wireless charging compatible” (as both technologies are sensitive to metal and thickness).
- Material: Choose cases made from silicone, TPU, polycarbonate, or natural leather.
- Thickness: Aim for a total thickness under 3mm for best results, especially near the top‑back area where the coil sits.
What to Avoid
- Metal Plates: Avoid any case with a built-in metal kickstand or a plate for a magnetic car mount.
- Battery Cases: These are a common source of both thickness and electronic interference.
- Multi-Layer “Tough” Cases: While great for protection, their bulk is often too much for NFC.
FAQs
Why does my card only work without a case?
Your case is likely too thick or contains metal/magnets. This blocks the weak magnetic field your phone uses for NFC (contactless) payments, causing the tap to fail.
Do metal cases block NFC and Apple Pay/Google Wallet?
Yes, absolutely. Metal cases are one of the most common reasons NFC, Apple Pay, and Google Wallet fail to work. The metal interferes with the signal and prevents a connection.
What is an on-metal NFC tag and when should I use it?
An on-metal NFC tag has a special ferrite backing that shields it from metallic interference. You should use it whenever you need to place an NFC tag on a metal surface like a steel desk, an aluminum laptop, or a refrigerator. Once you have the right tag, you can learn how to program it on Android or write a vCard to it with your iPhone or Android.
Will a MagSafe wallet cause NFC interference?
Yes, it can. The magnets in the wallet and the extra thickness of the cards can interfere with your phone’s NFC signal. It is best to remove the wallet before making a contactless payment.
Does NFC drain my phone’s battery?
When idle, NFC uses virtually no power. It only draws a tiny amount of battery when it’s actively scanning or communicating with a reader. You can safely leave it on all day without noticing any impact on battery life.
Can NFC damage my physical credit cards?
No. The magnetic field used by NFC is extremely weak and is not strong enough to damage the magnetic stripe or chip on your credit cards, even if they are kept together in a wallet case.
Conclusion: Tap and Go with Confidence
Navigating the world of contactless payments and NFC business cards should be simple, and it can be. As we’ve seen, the most common reason for a tap to fail is a phone case that’s either too thick or contains metal. By understanding how NFC works and knowing where your phone’s antenna is located, you can solve most issues in seconds.
Whether you’re switching to a slimmer case, using an on-metal tag for a project, or simply removing your MagSafe wallet before you pay, you’re now in control. You have the knowledge to diagnose the problem and apply the right fix, ensuring your next tap is quick, successful, and frustration-free.
Meet Oladepo Babatunde, a technical writer and researcher who makes digital business cards easy to use in the real world. As the founder of CardAdviceHub.com, Oladepo turns tap‑to‑connect tech into clear, reliable workflows—covering NFC/QR setup, troubleshooting, platform comparisons, and practical design tips. He draws on a Higher National Diploma in Computer Science and more than a decade of writing experience since 2014 to test cards, apps, and accessories hands‑on, then share step‑by‑step guides with screenshots, checklists, and templates you can follow in minutes. When he’s not filming tutorials, he’s building resources that help solo creators and teams launch faster—no code required. CardAdviceHub focuses on informational how‑tos and does not publish financial advice.
Areas of focus: NFC tags and chips (NTAG213/215/216), iPhone/Android setup, QR best practices, platform integrations (Sheets, HubSpot, Zapier), event signage and accessories.
How I test: Real devices, repeated tap/read tests with different cases/materials, screenshots and videos for every step, and “first‑try” reliability checks.
Editorial standards: Every how‑to is reproducible, updated when apps change, and clearly labels any affiliate relationships. No financial advice.
Contact: info@cardadvicehub.com (or contact us)



