Wondering what an NFC business card is and how do NFC business cards work with modern phones like the iPhone and Android? This comprehensive guide breaks it all down. We’ll explore everything from the basic technology behind the NFC business card to DIY options and a review of the best NFC business cards for 2025, giving you all the information you need to make a powerful first impression.
Author’s Note: I wrote this guide based on first-hand experience testing NTAG213, NTAG215, and NTAG216 tags on an iPhone 15 Pro (iOS 18) and a Google Pixel 8 (Android 15). My goal is to give you clear, practical advice you can trust.
Quick Start: The 90-Second Guide
An NFC business card is a physical card with a tiny, powerless computer chip inside called an NFC tag. When you tap this card against a modern smartphone, it instantly opens a link to your digital profile, contact card (vCard), or website. No special app is needed on recent iPhones or most Android phones. It’s a fast, modern way to share your information.
An NFC business card is a physical card with a passive NFC tag inside (typically NTAG213/215/216). When a modern smartphone comes within a few centimeters, the phone energizes the tag at 13.56 MHz (ISO/IEC 14443), reads an NDEF record (usually a URL or vCard), and opens the appropriate app, as detailed in the NFC Forum technical overview. On iPhone XS/XR and newer, this works via background tag reading with a user tap; most Android phones behave similarly when the screen is on and NFC is enabled. This guide will cover everything from free DIY options to our review of the best NFC business cards for 2025.
How Do NFC Business Cards Work?
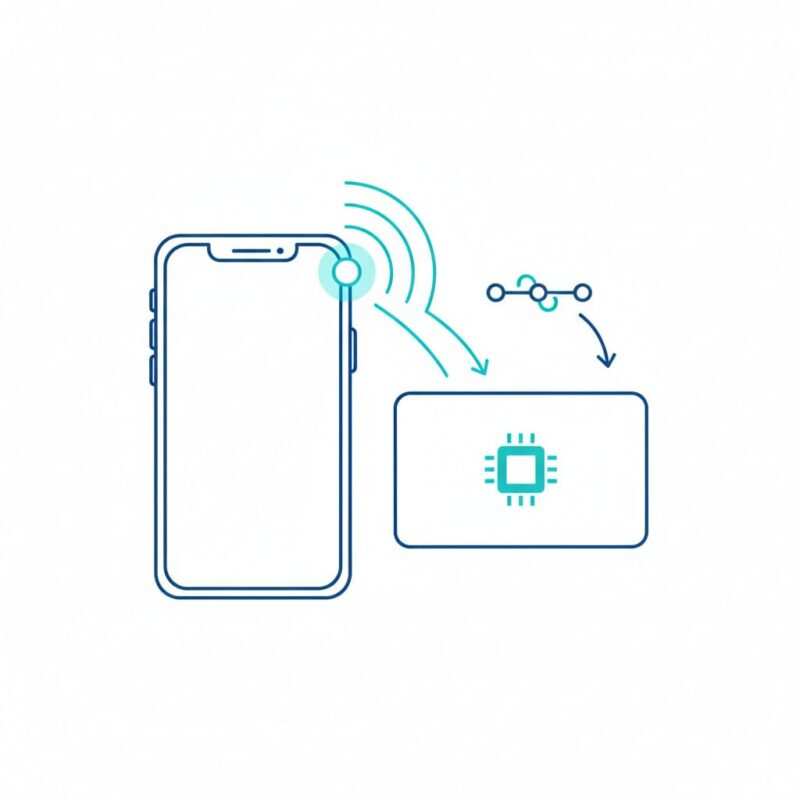
The magic is in the technology, but it’s simple to understand. The entire exchange happens in less than a second, powered by a process called electromagnetic induction.
- The Tag: Inside the card is a passive NFC tag (popular types from manufacturers like NXP Semiconductors include NTAG213/215/216). “Passive” means it has no battery or internal power source. It lies dormant until it comes near an active NFC device, like your phone. The NTAG215, for example, is the same type of chip widely reported in online communities to be used in applications like Nintendo’s Amiibo figures, known for its reliability.
- The Data: The tag stores a small piece of data called an NDEF (NFC Data Exchange Format) record. The amount of available tag memory is small—according to NXP, the user memory for NTAG213/215/216 tags is approximately 144, 504, and 888 bytes, respectively. This is a read/write chip, meaning you can update the data on it if needed.
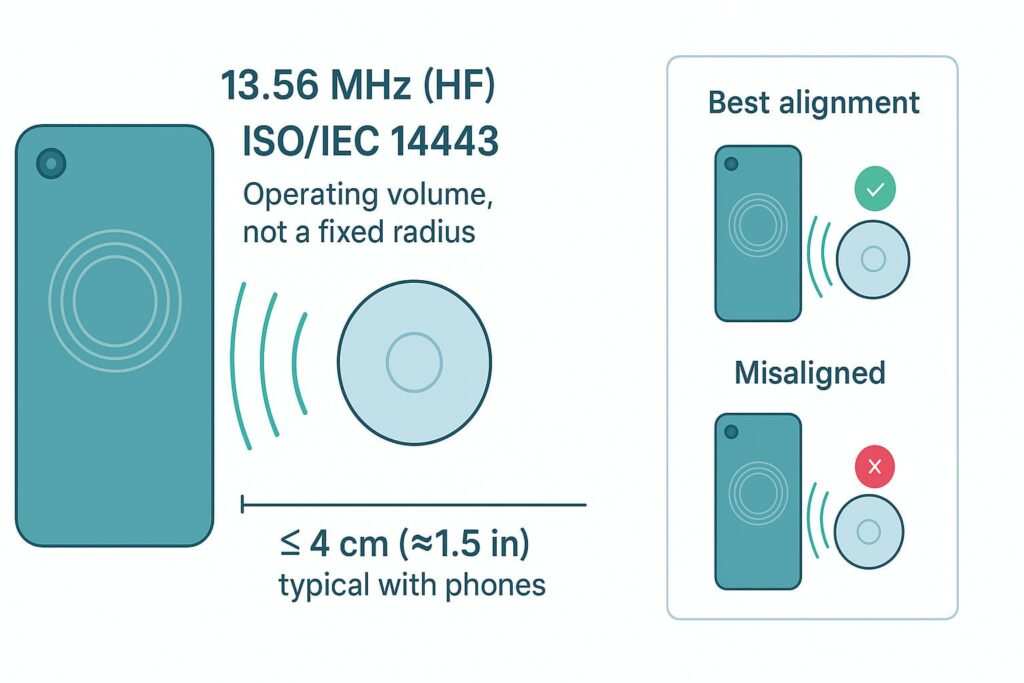
- The Tap: When you tap the card on a phone, the phone’s NFC antenna, which is an active device, sends out a radio signal at a frequency of 13.56 MHz. This is based on the global ISO/IEC 14443 standard, the same trusted technology used in contactless payment cards and transit passes. This signal creates a small magnetic field that energizes the tag’s antenna.
- The Transfer: Once powered, the tag instantly sends its stored NDEF data back to the phone. The phone’s operating system reads this data and opens the appropriate app—your web browser for a URL or your Contacts app for a vCard—all without you needing to press a button.
vCard vs. URL: Which is Better to Encode?
- vCard (Contact File): This option tries to save your contact info directly to the phone’s address book. It’s a direct method of contact sharing, but can sometimes be blocked by a phone’s security settings. It’s also static; if your number changes, the card is outdated.
- URL (Web Link): This is the more popular and flexible option. The NFC tag directs the user to a web page (your digital profile). From there, they can choose to save your contact info, visit your social links, or view your portfolio. You can update this online profile anytime without ever changing the card.
Now that you understand the basic mechanics, let’s look at how this technology works specifically on the world’s most popular smartphones.
Can an iPhone read an NFC business card?

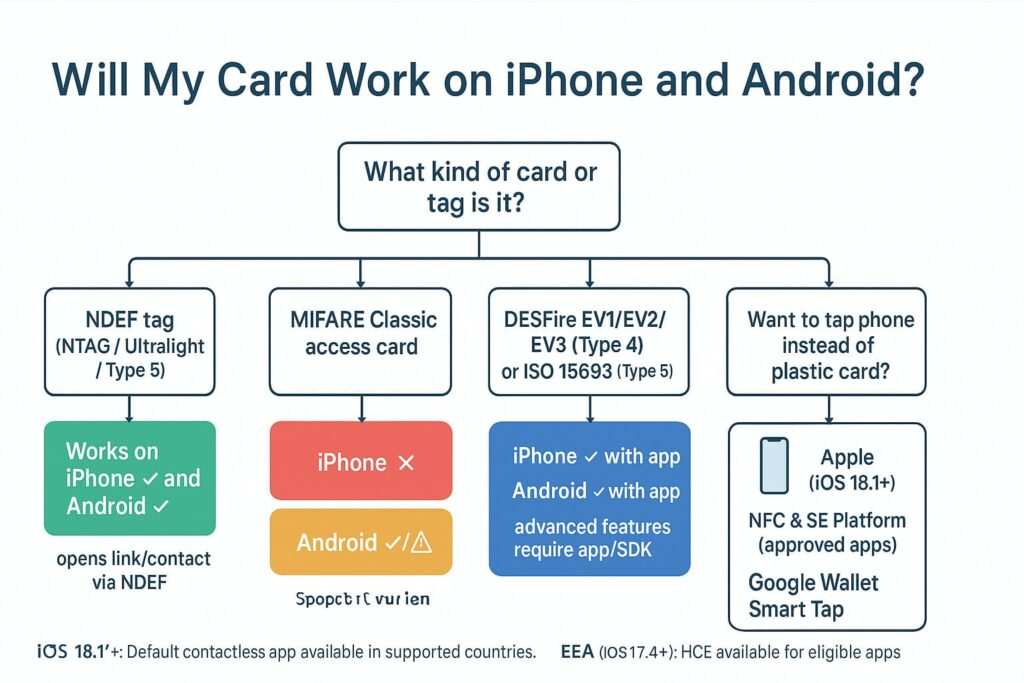
Yes, an NFC business card for an iPhone works seamlessly. On an iPhone XS, XR, and all newer models from Apple, the device can read NFC tags without needing a separate app; this is called background tag reading. On supported iPhones, a banner appears after the tap; the user must tap this notification to proceed, as there is no silent auto-launch for security reasons. It’s also important to note that background reading is temporarily disabled in scenarios like when Apple Wallet is in use or the phone is in airplane mode.
For older models like the iPhone 7, 8, and X, you need to use a third-party app from the App Store that utilizes Apple’s Core NFC framework to enable tag reading and writing.
How to Use NFC on an iPhone
- Unlock the iPhone. The screen must be on.
- Hold the card near the top edge of the phone, by the front camera and speaker area. This is where the NFC reader is located.
- A notification will pop up at the top of the screen. Tap this notification to open the link.
Tip: On iPhones, the NFC read area is near the top edge; place the tag by the front camera/speaker area.
While the process is seamless on modern iPhones, Android devices offer similar ease of use with a few minor differences.
NFC Business Card on Android: How It Works
Most modern Android phones have NFC capability, making an NFC business card on Android just as easy to use. For it to work, NFC must be turned on in your settings, and the phone’s screen must be on and unlocked.
How to Use NFC on an Android Phone
- Unlock your phone’s screen.
- Enable NFC. Go to Settings > Connections (or Connected devices) and make sure the NFC toggle is on. This process is officially documented in the Android NFC basics guide for developers.
- Tap the card to the back of the phone. The antenna location varies by model—try near the camera or the center back of the phone.
With compatibility covered, it’s crucial to remember that the card itself is just a key; the destination it unlocks is what truly matters.
Digital NFC Business Card: What You Actually Share
It’s important to know that the physical NFC card is just the key. The real value is the digital NFC business card profile it unlocks. A weak digital profile can ruin a great first impression.
Designing a High-Converting Digital Profile
Your digital landing page should be clean, professional, and mobile-friendly. A fast-loading page with a good user experience is crucial; for developers, this means optimizing for Core Web Vitals like Interaction to Next Paint (INP).
- Lead with Value: Start with a clear photo of yourself, your name, and your job title.
- Provide Multiple Contact Options: Include links to your key social media profiles (like LinkedIn), your email, and your phone number.
- Include Clear Calls-to-Action (CTAs): Use buttons like “Save Contact,” “Book a Meeting,” or “View My Work.” Make it obvious what you want the person to do next.
- Showcase Your Work: Add a gallery, videos, or links to your portfolio to provide more context and value.
A professional profile makes a huge difference, but you don’t necessarily need to pay for a service to get started.
NFC business card free: How to Make Your Own
Want a free NFC business card? You can make one yourself for just a few dollars. Here’s how to make an NFC card in just a few minutes.
Choosing the Right Blank NFC Tag
Based on specifications from the manufacturer NXP, here are the common choices:
- NTAG213 (144 bytes user memory): Perfect for most short URLs. This is the most common and affordable option.
- NTAG215 (504 bytes user memory): Offers more tag memory for longer links or if you want to experiment with a vCard that has more fields.
- NTAG216 (888 bytes user memory): Provides the most memory, but is often overkill for a simple business card.
How to Create Your DIY Card
- Step 1: Buy Blank NFC Tags. You can buy NFC sticker tags online very cheaply. Look for NTAG213 or NTAG215 stickers. They are small and can be stuck to the back of any existing business card.
- Step 2: Encode Your Tag. You need an app to read/write your information onto the tag.
- On Android: Search the Google Play Store for “NFC Tools” or a similar app. You can write a URL to the tag in seconds.
- On iPhone: Since iOS 13, iPhone 7 and newer can write NDEF to tags via Core NFC–based apps; a popular choice is “NFC Tools.”
- Step 3: Test It. Always test your tag on both iPhone and Android to ensure it works perfectly before you start sharing it. Only encode links to websites you trust.
DIY is a great way to experiment, but the apps you use are central to the experience, whether you’remaking your own or using a professional service.
The Role of an NFC Business Card App
An NFC business card app serves two distinct purposes depending on your needs.
- Utility Apps for DIY: For those making their own cards, apps like “NFC Tools” are essential. They act as a writer, allowing you to encode data (like a URL) onto a blank NFC tag. They are purely functional and don’t manage a digital profile.
- Platform Apps for Professional Cards: When you buy a card from a service like Popl or Blinq, their dedicated app is your command center. You use it to create and instantly update your digital profile, view analytics (how many taps your card gets), and manage the leads you capture. This kind of app is a complete networking tool, not just a tag writer.
Understanding the role of the app helps you decide whether to DIY or to choose a professional service.
NFC Business Card Maker: Best Practices
If you prefer a professional solution, many companies offer NFC business card maker services. When choosing one, look beyond the physical card and evaluate the software platform.
- Customizable Profile: The platform should offer an intuitive drag-and-drop editor so you can easily update your digital profile anytime without technical skills.
- QR Code Fallback: A dynamically generated QR code linked to the same profile should be included on the card. This ensures anyone with a smartphone can access your information, even without NFC.
- Lead Capture: A good service allows you to add a simple contact form to your profile, making it easy to collect information from new connections with their permission.
- Apple Wallet / Google Wallet: The ability to share your digital card and have people save it to their phone’s Apple Wallet or Google Wallet is a powerful, modern feature.
- Analytics: See how many people have tapped or scanned your card, what links they clicked, and where they are located. This data helps you understand your networking ROI.
- Clear Privacy Policy: Understand how your data and your contacts’ data are being used and protected.
The material of your card is just as important as the software behind it, especially when you’re aiming for a premium feel.
NFC Business Card Metal: Pros, Cons, and On-Metal Tags

A metal NFC business card looks incredibly premium and is very durable. However, there’s a big catch: metal blocks NFC signals.
- Pros: Amazing feel, very durable, makes a strong impression.
- Cons: Standard NFC tags will not work when placed on a metal surface because the metal interferes with the magnetic field.
The Solution: To make a metal card work, manufacturers must use special on-metal NFC tags. These tags have a thin, built-in ferrite shield layer—a material that absorbs and redirects the interference—protecting the signal and allowing the card to be read properly (Source: NFC Tag/Antenna design guides). It’s important to note that this shielding can sometimes slightly reduce the maximum scan distance compared to a standard tag on a non-metal surface. If you are buying a metal card, confirm with the seller that it uses a dedicated on-metal tag.
Other Premium Materials
Materials like wood, bamboo, and thicker PVC plastics are generally NFC-friendly and do not require special shielding, offering other unique and sustainable options.
With so many options on the market, it helps to know which providers are leading the pack.
Best NFC Business Cards 2025: What to Look For
To find the best NFC business cards in 2025, focus on the features first, then the brand. A great platform should offer:
- A reliable NTAG213 (or better) chip.
- An easy-to-use profile editor.
- A QR code option on the card.
- Analytics and contact management features.
- Team management options for businesses.
- Support for Apple Wallet and Google Wallet passes.
- A fair price with clear shipping information.
Here are a few well-known vendors in the market to give you examples of what’s available.
- Popl: A popular platform with an app-centric experience, a wide range of NFC products (cards, phone tags, badges), and robust team features for lead capture and CRM integration.
- Linq: Offers a variety of sleek cards and other NFC products with a focus on highly customizable profiles, analytics, and enterprise-level team management.
- Blinq: Provides an iOS and Android app for creating digital cards that can be linked to physical NFC cards, with strong Apple Wallet support and integrations with tools like Salesforce and HubSpot.
- V1CE: Known for its premium and custom-designed physical cards, including 24k gold plated and full-metal options, that combine both NFC and a QR code.
- Tap Tag: Offers a wide variety of card materials and fully custom designs, including on-metal tags, with no required subscription for basic functionality.
Note: This is not an endorsement. Always check current pricing, features, and reviews before purchasing.
The rise of NFC cards naturally leads to the question of how they stack up against the now-ubiquitous QR code.
Are NFC cards better than QR codes?

Neither is “better”—they are just different tools for different situations. A smart approach uses both.
| Feature | NFC Business Card | QR Code |
|---|---|---|
| Ease of Use | Tap-to-open, feels seamless and magical. | Point camera to scan, universally understood. |
| Speed | Slightly faster, opens almost instantly. | Works from a distance (e.g., on a presentation slide). |
| Hardware | Requires a physical chip in the card. | Just ink on paper; can be printed anywhere for free. |
| Impression | Feels modern, high-tech, and premium. | Very practical and widely compatible. |
| Cost | Higher initial cost for the physical card. | Free to generate and print. |
| Durability | The chip is very durable (100k+ rewrites). | Can become unreadable if scratched or faded. |
A great strategy is to have both on your card. For context, QR code standards are managed by organizations like GS1, ensuring their universal reliability.
The technology’s similarity to “tap-to-pay” often raises questions about its other applications and security.
Do credit cards use NFC?
Yes. The “tap-to-pay” or “contactless” feature on your credit and debit cards uses the same core NFC technology (based on ISO/IEC 14443). However, payment cards have many extra layers of security based on the EMV (Europay, Mastercard, and Visa) standard. As detailed in EMVCo’s payment tokenisation explainer, contactless EMV cards generate a unique, one-time cryptogram per transaction. Mobile wallets (e.g., Apple Pay/Google Pay) additionally use network tokenization in combination with dynamic cryptograms, making them very safe for payments.
This connection to payments naturally leads to concerns about whether leaving NFC enabled on your phone is safe.
Is it risky to leave NFC on?
NFC’s risk profile is low because of the very short range and OS safeguards. iOS shows a banner you must tap; Android routes via intent dispatch and may prompt an app choice. As with QR codes, the main risk is tapping unknown tags that lead to phishing URLs—use the same link hygiene you would on the web.
Advanced Security Considerations
For enterprise users, some platforms offer enhanced security features like password protection for links or using dynamic URLs that change periodically. Some tags also support UID (Unique ID) authentication, but this is a lightweight measure and not a robust anti-cloning solution by itself; for real security, it must be paired with server-side validation.
Security is one aspect of durability; the physical and digital lifespan of the card is another.
How long do NFC business cards last?
NFC tags are surprisingly durable and have two different lifespans to consider: data retention and tag endurance. According to the manufacturer, NXP Semiconductors, their popular NTAG21x line has the following specifications, which you can verify on the official NTAG213/215/216 product page:
- Data Retention: This is how long the chip can hold your information without power. NXP specifies a data retention of 10 years.
- Tag Endurance (Write Cycles): This is how many times you can rewrite new information to the tag. The standard tag endurance is 100,000 write cycles, which is far more than anyone would ever need for a business card.
The physical card itself (PVC, metal, or wood) will likely wear out long before the chip does.
Environmental Factors and Physical Care
To maximize the life of your card, avoid bending it sharply, exposing it to extreme temperatures, or submerging it in water for long periods, although most are water-resistant.
Despite their durability, NFC cards are not without their potential downsides and limitations.
What are the disadvantages of NFC card?
While they are great, NFC cards aren’t perfect. The potential downsides include:
- Compatibility: Not every phone has NFC, especially some older or budget Android models.
- Metal Interference: Standard tags don’t work on metal surfaces, requiring more expensive on-metal NFC tags.
- Proximity: You have to be very close to the phone for it to work, which can sometimes lead to an awkward “tap-dance” if you don’t know the right spot.
- Discovery: Some people may not know their phone has NFC or where to tap. Printing a small icon or “Tap here” text on the card can help guide them.
The Hybrid Solution: Combining NFC + QR
The best way to overcome all these disadvantages is to use a hybrid card. A physical card that has your name, an embedded NFC tag, and a printed QR code is the most reliable and future-proof networking tool.
Understanding these disadvantages helps clarify why having alternatives is always a good strategy.
What is the alternative to NFC cards?
If an NFC card isn’t right for you, there are other great modern options:
- QR Codes: A simple QR code (like those using the GS1 Digital Link standard) can link to your digital profile and can be shown on your phone screen or printed anywhere.
- Apple/Google Wallet Passes: You can create a digital business card that people can save directly to their phone’s Apple Wallet or Google Wallet. This is convenient but can be a bit more complex to set up.
- A Simple URL: You can just text or email a link to your profile. It’s less impressive but highly effective.
- Traditional Paper Cards: A classic paper card with a QR code printed on it is still a very effective and low-cost tool.
This brings us to a fundamental question: in an increasingly digital world, is any form of business card still relevant?
Are business cards worth it anymore?
Yes, but the definition of a “business card” has evolved. Instead of carrying 100 static paper cards that get thrown away, you can carry one dynamic, smart NFC card. This hybrid approach provides a clear return on investment (ROI):
- Cost-Effective: You don’t have to keep reprinting cards when your details change. Just update your online profile.
- Eco-Friendly: It drastically reduces paper waste. Compared to the continuous printing of traditional cards, which contributes to deforestation and resource consumption, a single reusable NFC card is a more sustainable choice.
- Measurable ROI: Unlike a paper card, a smart card provides analytics. You can see how many people engaged with your card, giving you real data on your networking efforts.
- Effective Lead Capture: It makes it easy for people to save your info and for you to capture theirs through a contact form, syncing directly to your CRM.
Calculating the ROI of Your NFC Card
A simple way to think about ROI is to compare the cost of one NFC card (e.g., $50) to the lifetime cost of printing paper cards (e.g., $50 every year for new prints). More importantly, if the analytics and lead capture features of your smart card help you land just one client you might have otherwise lost, it has likely paid for itself many times over.
This powerful potential often brings people back to the idea of creating their own custom solution.
Can I make my own NFC business card?
Yes! As we covered in the DIY section, it’s easy and affordable. Just buy a blank NTAG sticker, use a free app on your phone (like NFC Tools) to write your profile URL to it, and stick it on any card you like. For the best results, always include your name and a printed QR code on the card itself as a backup.
Creative & Advanced DIY Uses
Beyond just a link, you can get creative. Program a tag to:
- Share your Wi-Fi network credentials.
- Open a specific playlist or video.
- Link directly to a payment app like Cash App or Venmo.
- Trigger a smart home routine.
These advanced applications showcase the versatility of NFC technology beyond simple networking.
Troubleshooting Common NFC Problems
Even with modern technology, you can run into hiccups. Here are solutions to common issues.
- Problem: The card isn’t being read.
- Solution: Make sure NFC is enabled on the Android phone. Try tapping different parts of the phone’s back, as the antenna location varies. Remove any thick phone cases or magnetic accessories like PopSockets that could be blocking the signal.
- Problem: The wrong app opens or an error appears.
- Solution: This can happen if the phone has multiple apps that can handle NFC actions. You may see a prompt to choose an app. For “No supported application” errors on Android, the tag might be empty, corrupted, or formatted in a way the phone doesn’t recognize. Try re-encoding the tag.
- Problem: The tap works on Android but not iPhone.
- Solution: Remember that the NFC reader on an iPhone is at the very top edge. Tapping the back of an iPhone won’t work. Also, ensure the iPhone is a compatible model (XS or newer).
FAQs
How do NFC cards work?
An NFC card contains a small, passive NFC tag that stores data like a web link in an NDEF record. When tapped against a smartphone, the phone’s NFC reader powers the chip and reads the data, automatically opening the link.
How do NFC business cards work on iPhone/Android?
On iPhone XS and newer, just tap the card to the top of the unlocked phone. On most Androids, tap the card to the back of the unlocked phone while NFC is enabled in settings.
How long do NFC cards last?
The chip inside has excellent data retention (10+ years) and tag endurance (100,000 rewrites). The physical card’s lifespan depends on its material.
Are NFC cards better than QR codes?
They serve different purposes. NFC is faster and feels more premium for in-person sharing. QR codes are more universal, work from a distance, and can be printed for free. The best cards have both.
Do credit cards use NFC?
Yes, “tap-to-pay” contactless cards use a more secure version of NFC technology based on ISO/IEC 14443.
Is it risky to leave NFC on?
The risk is very low due to the extremely short range. Just be careful not to tap your phone on unknown tags.
Can an iPhone read an NFC business card?
Yes, iPhone XS/XR and all newer models from Apple can read an NFC card without an app. Older models (7/8/X) require an app.
Best NFC business cards 2025?
The best card depends on your needs. Look for platforms like Popl, Linq, or Blinq that offer customizable profiles, analytics, and a QR code fallback.
NFC Business Card Metal: will it scan?
Only if it uses a special on-metal NFC tag with a ferrite shield to prevent the metal from blocking the signal.
NFC business card free: what are my options?
You can create your own for a very low cost by buying blank NTAG stickers online and using a free app like “NFC Tools” to encode your information onto them.
Final Thoughts: The Future of Your First Impression
In 2025, networking is about making a memorable, efficient, and lasting connection. The NFC business card represents a significant evolution from its paper predecessor, bridging the physical and digital worlds with a single tap. It’s more than just a gadget; it’s a powerful tool for modern professionals that is sustainable, measurable, and impressive.
By combining the seamless magic of NFC with the universal reliability of a QR code, you create a networking tool that works for everyone, every time. Whether you choose a premium pre-made card or a simple DIY solution, you’re not just sharing contact details—you’re demonstrating that you’re forward-thinking and ready for the future. The next time you meet a valuable connection, you’ll be ready to make an impression that truly lasts.
Meet Oladepo Babatunde, a technical writer and researcher who makes digital business cards easy to use in the real world. As the founder of CardAdviceHub.com, Oladepo turns tap‑to‑connect tech into clear, reliable workflows—covering NFC/QR setup, troubleshooting, platform comparisons, and practical design tips. He draws on a Higher National Diploma in Computer Science and more than a decade of writing experience since 2014 to test cards, apps, and accessories hands‑on, then share step‑by‑step guides with screenshots, checklists, and templates you can follow in minutes. When he’s not filming tutorials, he’s building resources that help solo creators and teams launch faster—no code required. CardAdviceHub focuses on informational how‑tos and does not publish financial advice.
Areas of focus: NFC tags and chips (NTAG213/215/216), iPhone/Android setup, QR best practices, platform integrations (Sheets, HubSpot, Zapier), event signage and accessories.
How I test: Real devices, repeated tap/read tests with different cases/materials, screenshots and videos for every step, and “first‑try” reliability checks.
Editorial standards: Every how‑to is reproducible, updated when apps change, and clearly labels any affiliate relationships. No financial advice.
Contact: info@cardadvicehub.com (or contact us)